Neurodevelopmental Assessments
Conners Continuous Auditory Test of Attention (Conners CATA)
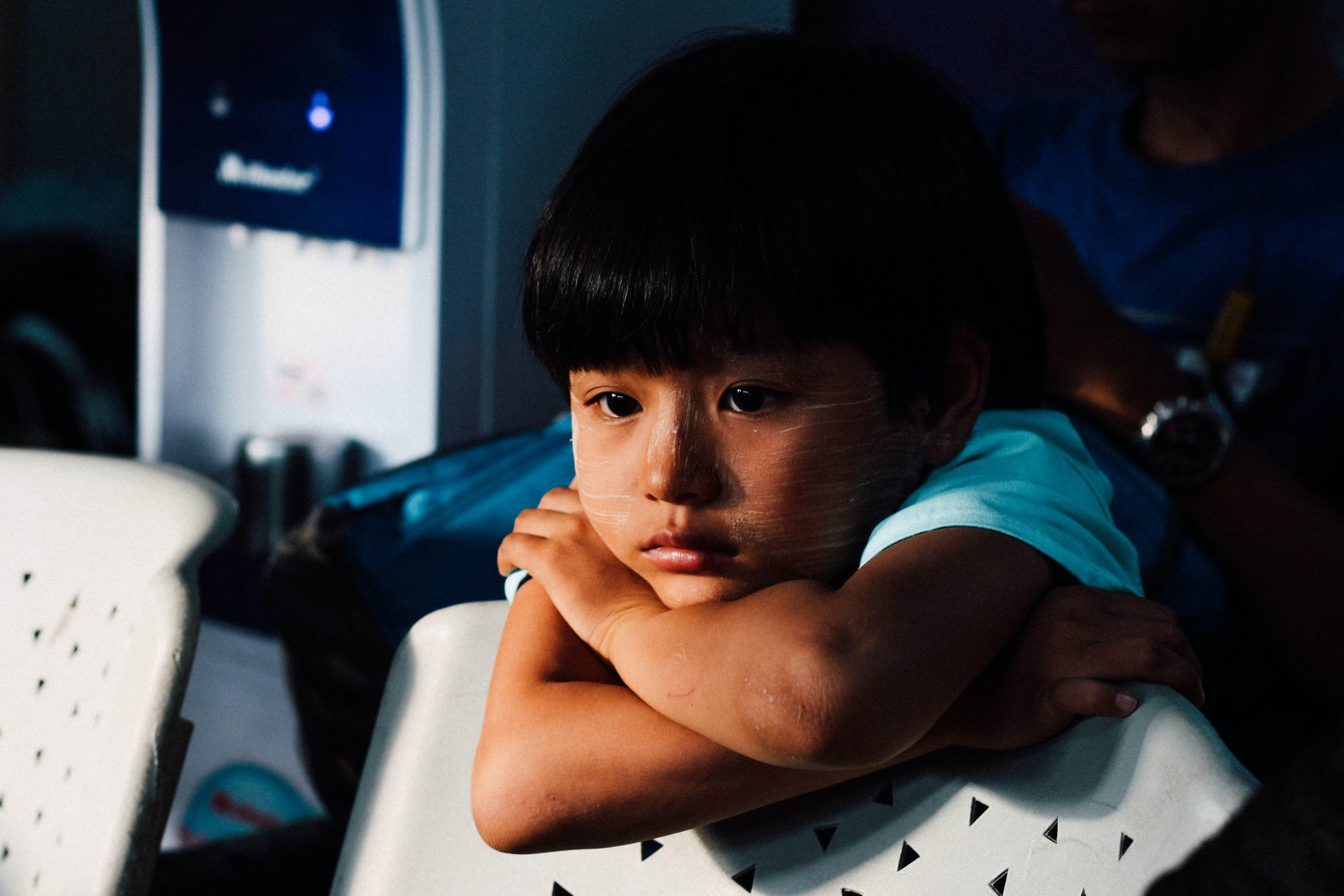
How do you know if your child’s level of inattentiveness and impulsivity is normal or a sign of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)? Although it is quite normal for children to be inattentive and impulsive, children with ADHD tend to display attention-related problems in a more severe pattern across more than one context.
If your child shows indicators of inattention and impulsivity, you might want to consider the Conners Continuous Auditory Test of Attention™ (Conners CATA™). It is appropriate for children and adolescents aged 8 and up.
The Conners CATA™ measures a child’s performance in areas of auditory processing and attention-related problems, specifically inattentiveness, impulsivity, and sustained attention. This is attained by administering a 14-minutes performance-based task on a computer to test the three domains of attention:
Ψ Inattentiveness: Inability to focus on something
Ψ Impulsivity: Tendency to act without thinking
Ψ Sustained Attention: Ability to maintain focus on a task for long periods
At the end of the test, the child’s score will be recorded and compared with the normative scores of their age, group and gender. This makes it a useful tool for evaluating attention disorders and neurological functioning.
The Conners CATA™ is frequently used to rule out ADHD and other attention-related neurological issues. It provides objective information about the child’s performance in attention tasks, complementing information obtained from rating scales such as the Conners (3rd edition) or Connors Continuous Performance Test (CPT). It is also effective for determining where a child’s attention-related strengths and weaknesses lie (e.g., if the child has a greater problem with impulsivity or sustained attention). Our child psychologist will then use this information to pinpoint areas in which a child is struggling and create intervention programs that are tailored to the child's specific needs.
However, it is crucial to note that the Conners CATA™ should not be used with children under the age of 8 as the assessment items are less age-appropriate, potentially leading to an inaccurate assessment. In that case, what happens if your child is below 8 years old? This is where the Kiddie Tests come into play to assess attention-related problems in children aged 4 to 7 years of age. The Conners Kiddie Continuous Performance Test (K-CPT; for ages 4-5 years) or the Conners Kiddie Continuous Performance Test 2nd edition (Conners K-CPT 2; for ages 4-7) can act as a substitute and a more appropriate test for children below 8 years of age.
Conners’ CATA is appropriate for children and adolescents 8 years of age and above.
It takes around 14 minutes to complete the assessment.